In the modern large-scale industrial production system, the packaging line, as a key link connecting product processing and finished product warehousing, has evolved from traditional manual operation into an efficient production system integrating mechanical automation, intelligent control, and data management. It not only completely addresses the pain points of low efficiency and high error rate in manual packaging but also becomes a core equipment for enterprises to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance product standardization. Widely used in food and beverage, pharmaceutical and healthcare, daily chemical and beauty, electronic and electrical appliances and other industries, it provides solid support for flexible production in the Industry 4.0 era.
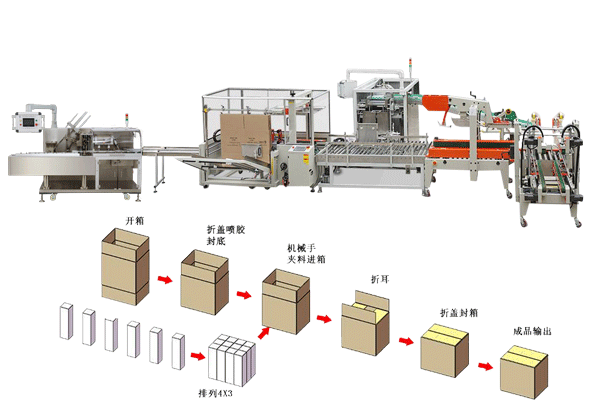
The core working principle of the packaging line is to complete a series of processes such as automatic sorting, positioning, packaging, sealing, and labeling of products through the coordinated operation of preset programs and mechanical structures, realizing the full-process automated processing from single products to standardized packaging boxes. A complete intelligent packaging line usually consists of core equipment and auxiliary systems: core equipment includes product conveyor lines, sorting and arranging mechanisms, packaging execution units (such as robotic arms, grasping-type packaging devices), carton sealers (adhesive tape sealing or hot melt adhesive sealing), labeling machines, palletizers, etc.; auxiliary systems include PLC control systems, visual inspection systems, data acquisition modules, and MES (Manufacturing Execution System) interfaces to ensure precise coordination and traceability of the entire process.
In application scenarios, the packaging line demonstrates strong adaptability and flexibility. In the food and beverage industry, for standardized products such as bottled water and carbonated drinks, the packaging line can achieve high-speed packaging of 30-120 boxes per minute. It avoids bottle scratches through flexible grasping mechanisms and completes real-time printing of production dates, batches and other information with coding machines. In the pharmaceutical industry, considering the cleanliness and safety requirements of drug packaging, the packaging line adopts sterile-grade materials and closed design, combined with visual inspection systems to check the quantity of drugs and whether instructions are missing, ensuring each box of products meets GMP standards. In the electronic and electrical appliances industry, facing irregularly shaped small household appliances and components, the intelligent packaging line realizes rapid switching and packaging of multi-specification products through programmable robotic arms and customized fixtures, with switching time only a few minutes, meeting the production needs of multi-variety and small-batch.
Compared with traditional manual packaging, the technical advantages of intelligent packaging lines are particularly prominent. Firstly, there is a leap in efficiency. The single-shift efficiency of manual packaging is usually 200-500 boxes, while the automated packaging line can reach up to 1,500 boxes per hour and can operate continuously for 24 hours, greatly improving production capacity. Secondly, there is cost optimization. In the long run, the packaging line can replace the workload of 5-10 workers, reducing labor costs and management costs, while reducing product loss and packaging waste caused by human operation errors. Thirdly, there is quality assurance. Through visual inspection, precise positioning and other technologies, the packaging error rate can be controlled below 0.01%, ensuring the quantity and placement of each box of products are completely consistent, and improving the qualified rate of product delivery and brand image. Finally, there is data management capability. The packaging line can real-time collect data such as packaging quantity, equipment operation status, and fault early warning, and upload it to the enterprise management platform through the MES system, providing data support for production scheduling and inventory management, and helping enterprises achieve lean production.
With the in-depth development of industrial intelligence, packaging lines are upgrading towards smarter, more flexible, and greener directions. In terms of intelligence, the application of AI visual recognition technology enables the packaging line to automatically identify product specifications and packaging forms, adapting to multi-category production without manual adjustment. In terms of flexibility, modular design allows the packaging line to flexibly increase or decrease equipment units according to enterprise production capacity needs, meeting the full-cycle needs from small-batch trial production to large-scale mass production. In terms of greenization, the application of technologies such as energy-saving motors, degradable packaging material adaptation design, and waste heat recovery systems enables the packaging line to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact while improving efficiency.
From the perspective of industry development trends, future packaging lines will pay more attention to integration with technologies such as industrial Internet and digital twins, optimize production processes through virtual simulation, and realize remote equipment monitoring and predictive maintenance. At the same time, targeting the special needs of emerging fields such as new energy and high-end manufacturing, customized packaging solutions will become a market hotspot. For example, anti-collision packaging lines designed for new energy battery modules and anti-static packaging systems built for precision electronic components.
As a key link in the modern industrial production chain, the intelligent packaging line is not only a tool for efficiency improvement but also an important carrier for enterprises to achieve digital transformation and enhance core competitiveness. With the continuous iteration of technology and the expansion of application scenarios, the packaging line will play a more important role in promoting the high-quality development of industrial production, becoming an efficient bridge connecting production and the market.